Akkadian|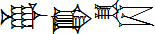 Historical
Historical
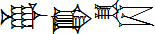 Historical
Historical
What is it?
Akkadian was a semitic language spoken in Mesopotamia (modern Iraq and Syria) between about 2,800 BC and 500 AD. It was named after the city of Akkad and first appeared in Sumerian texts dating from 2,800 BC in the form of Akkadian names.
The Akkadian cuneiform script was adapted from Sumerian cuneiform in about 2,350 BC. At the same time, many Sumerian words were borrowed into Akkadian, and Sumerian logograms were given both Sumerian and Akkadian readings. In many ways the process of adapting the Sumerian script to the Akkadian language resembles the way the Chinese script was adapted to write Japanese. Akkadian, like Japanese, was polysyllabic and used a range of inflections while Sumerian, like Chinese, had few inflections.
A large corpus of Akkadian texts and text fragments numbering hundreds of thousands has been excavated. They include mythology, legal and scientific texts, correspondence and so on. During the 2nd millenium BC the Akkadian language developed into two variants, Assyrian and Babylonian, in Assyria and Babylon.
Akkadian became the lingua franca of the ancient Near East, but started to be replaced by Aramaic by the 8th century BC. After that it continued to be used mainly by scholars and priests and the last known example of written Akkadian dates from the 1st century AD.
Alphabet:
Sample Text:

Tips: www.ancientscripts.com
Source: www.omniglot.com

Nenhum comentário:
Postar um comentário